网络学习利器—hping3
-c --count packet count
-i --interval wait (uX for X microseconds, for example -i u1000)
--fast alias for -i u10000 (10 packets for second)
--faster alias for -i u1000 (100 packets for second)
--flood sent packets as fast as possible. Don't show replies.
-n --numeric numeric output
-q --quiet quiet
-I --interface interface name (otherwise default routing interface)
-V --verbose verbose mode
-D --debug debugging info
-z --bind bind ctrl+z to ttl (default to dst port)
-Z --unbind unbind ctrl+z
--beep beep for every matching packet received
Mode
default mode TCP
-0 --rawip RAW IP mode
-1 --icmp ICMP mode
-2 --udp UDP mode
-8 --scan SCAN mode.
Example: hping --scan 1-30,70-90 -S www.target.host
-9 --listen listen mode
IP
-a --f spoof source address
--rand-dest random destionation address mode. see the man.
--rand-source random source address mode. see the man.
-t --ttl ttl (default 64)
-N --id id (default random)
-W --winid use win* id byte ordering
-r --rel relativize id field (to estimate host traffic)
-f --frag split packets in more frag. (may pass weak acl)
-x --morefrag set more fragments flag
-y --dontfrag set don't fragment flag
-g --fragoff set the fragment offset
-m --mtu set virtual mtu, implies --frag if packet size > mtu
-o --tos type of service (default 0x00), try --tos help
-G --rroute includes RECORD_ROUTE option and display the route buffer
--lsrr loose source routing and record route
--ssrr strict source routing and record route
-H --ipproto set the IP protocol field, only in RAW IP mode
ICMP
-C --icmptype icmp type (default echo request)
-K --icmpcode icmp code (default 0)
--force-icmp send all icmp types (default send only supported types)
--icmp-gw set gateway address for ICMP redirect (default 0.0.0.0)
--icmp-ts Alias for --icmp --icmptype 13 (ICMP timestamp)
--icmp-addr Alias for --icmp --icmptype 17 (ICMP address subnet mask)
--icmp-help display help for others icmp options
UDP/TCP
-s --baseport base source port (default random)
-p --destport [+][+]<port> destination port(default 0) ctrl+z inc/dec
-k --keep keep still source port
-w --win winsize (default 64)
-O --tcpoff set fake tcp data offset (instead of tcphdrlen / 4)
-Q --seqnum shows only tcp sequence number
-b --badcksum (try to) send packets with a bad IP checksum
many systems will fix the IP checksum sending the packet
so you'll get bad UDP/TCP checksum instead.
-M --setseq set TCP sequence number
-L --setack set TCP ack
-F --fin set FIN flag
-S --syn set SYN flag
-R --rst set RST flag
-P --push set PUSH flag
-A --ack set ACK flag
-U --urg set URG flag
-X --xmas set X unused flag (0x40)
-Y --ymas set Y unused flag (0x80)
--tcpexitcode use last tcp->th_flags as exit code
--tcp-mss enable the TCP MSS option with the given value
--tcp-timestamp enable the TCP timestamp option to guess the HZ/uptime
Common
-d --data data size (default is 0)
-E --file data from file
-e --sign add 'signature'
-j --dump dump packets in hex
-J --print dump printable characters
-B --safe enable 'safe' protocol
-u --end tell you when --file reached EOF and prevent rewind
-T --traceroute traceroute mode (implies --bind and --ttl 1)
--tr-stop Exit when receive the first not ICMP in traceroute mode
--tr-keep-ttl Keep the source TTL fixed, useful to monitor just one hop
--tr-no-rtt Don't calculate/show RTT information in traceroute mode
ARS packet description (new, unstable)
--apd-send Send the packet described with APD (see docs/APD.txt)
先运行服务器端,在 12345 端口上监听。
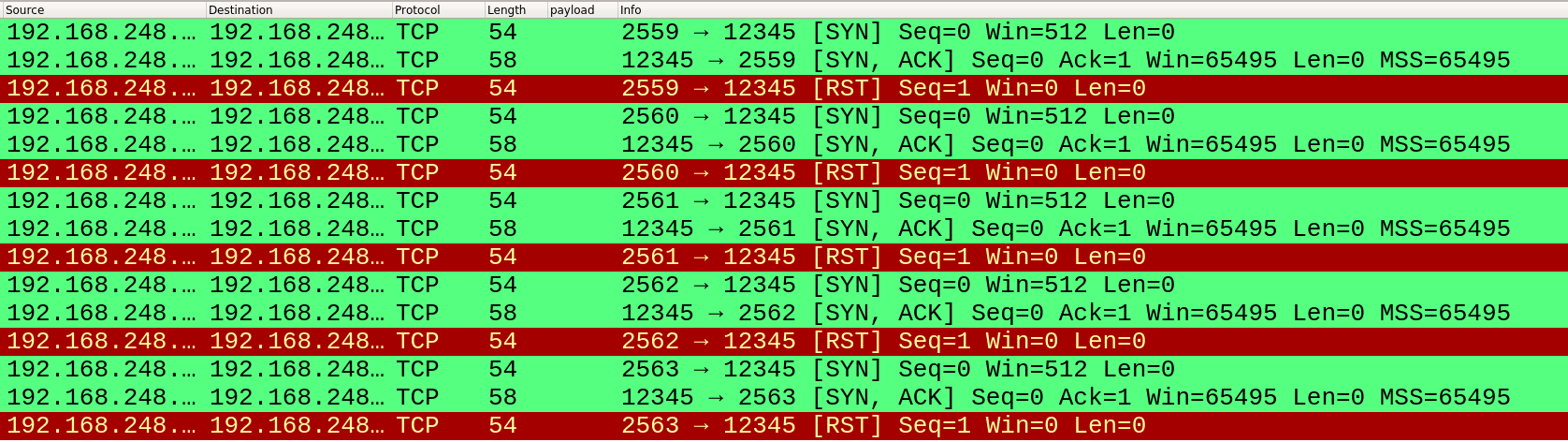
1)向 192.168.248.128 (本机 ens33 网卡的 IP 地址)的 12345 端口发送 5 个 SYN 报文
hping3 -S 192.168.248.128 -p 12345 -c 5
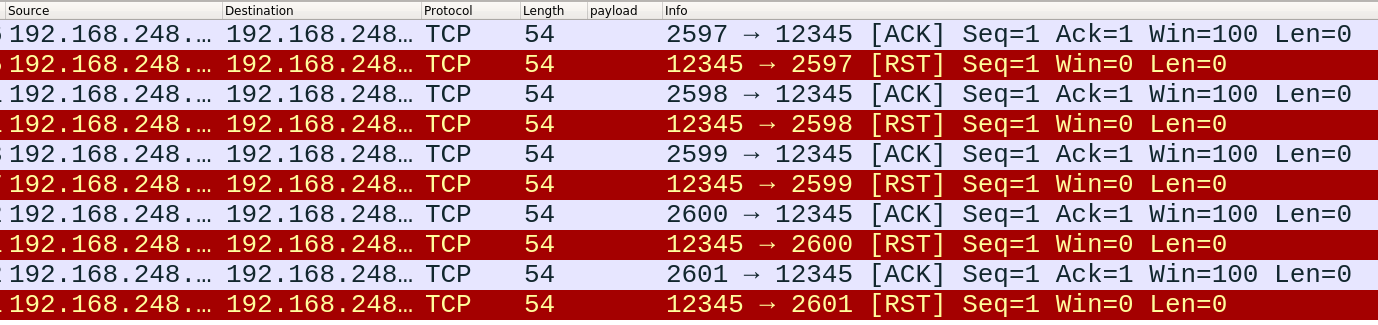
2)向 192.168.248.128 (本机 ens33 网卡的 IP 地址)的 12345 端口发送 5 个 ACK 报文,且窗口大小为 100
hping3 -A 192.168.248.128 -p 12345 -c 5 -w 100
注意:
我们向开放的 12345 端口发送 SYN 报文,得到的回复是 SYN+ACK 报文,即第二次握手;而发送 ACK 报文,则得到的回复是 RST 。这两种情况能够反应出端口的开放和过滤状态:
发送 SYN 报文:
行为 状态 数次重发未响应 filtered 收到ICMP不可达错误 filtered SYN/ACK open RST closed 发送 ACK 报文:
行为 状态 收到RST报文 unfiltered(open/closed) 未响应 filtered ICMP不可达 filtered 也就是说,我们可以通过向指定端口发送 SYN 或 ACK 报文来检测该端口的状态,这称为端口扫描 。
另外,关于报文过滤,参见本博客另一篇文章——包过滤工具iptables
3)端口扫描模式
扫描 baidu.com 的 75~85 和 12345 端口:
#hping3 --scan 75-85,12345 -S baidu.com
Scanning baidu.com (39.156.66.10), port 75-85,12345
12 ports to scan, use -V to see all the replies
+----+-----------+---------+---+-----+-----+-----+
|port| serv name | flags |ttl| id | win | len |
+----+-----------+---------+---+-----+-----+-----+
80 http : .S..A... 128 27907 64240 46
All replies received. Done.
Not responding ports: (75 ) (76 ) (77 rje) (78 ) (79 finger) (81 ) (82 ) (83 ) (84 ) (85 ) (12345 )
4)flood 泛洪攻击
向 127.0.0.1:12345 发起泛洪攻击,源 IP 随机:
hping3 127.0.0.1 -S -p 12345 --flood --rand-source
5)指定源端口为 12345,源 IP 为 1.1.1.1:
hping3 -S baidu.com -a 1.1.1.1 -s 12345
或
hping3 -S baidu.com --spoof 1.1.1.1 --baseport 12345
默认情况下源 IP 为主机地址,源端口随机
6)传输文件
Hping3 支持通过 TCP/UDP/ICMP 等包来进行文件传输。相当于借助 TCP/UDP/ICMP 包建立隐秘隧道通讯。实现方式是开启监听端口,对检测到的签名(签名为 --listen 后面输入的字符串)的内容进行相应的解析。在接收端开启服务:
#hping3 127.0.0.1 --listen signature --safe --icmp
监听 ICMP 包中的签名,根据签名解析出文件内容。在发送端使用签名打包的 ICMP 包发送文件:
hping3 127.0.0.1 --icmp -d 100 --sign signature --file ./data
注意两点:1)必须指定数据长度 -d ;2)签名字符串必须和接收端相同,这里是字符串 signature 。
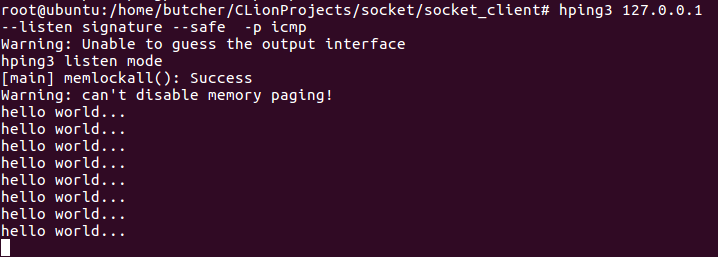
不过没人会使用这种方式来传送文件,因为它是明文发送的:

--safe 保证的是丢失重传,而不是安全性。
